Sunscreen oil – why you need extra protection
Sunscreen oil is a very popular choice among sun lovers who want a tanned and radiant skin. However, as tempting as it may be to apply a “fragrant layer” that promises a faster tan, it usually does not provide sufficient protection from ultraviolet rays. At the same time, many people want to avoid thick creams that leave white marks, so they turn to light oils that seem more practical. The question is, can we rely solely on sunscreen oil when we want to maintain skin health? Dermatologists themselves emphasize that it is crucial to have a good understanding of how the sun’s rays affect the skin and what our real needs for protection are. Below, we will explore what to consider when using sunscreen oil, how UVA and UVB rays work, what additional measures should be taken to enjoy the sun safely, and how natural products, such as aloe vera, fit into a holistic approach to skin protection and recovery. If you wanted detailed and verified information, keep reading!
Why is sun protection important?
Although the sun’s rays bring many benefits (vitamin D synthesis, mood improvement, natural light), they can be dangerous if not handled with care. The two main types of ultraviolet (UV) rays are UVA and UVB. While UVB rays mostly affect the surface layers of the skin and are mainly responsible for sunburn and redness, UVA rays penetrate deeper, accelerate skin aging and promote the formation of pigment spots.
Prolonged exposure to the sun without adequate protection increases the risk of melanoma and other forms of skin cancer, and in addition to the health aspect, it also significantly accelerates the visible aging of the skin. The loss of collagen and elastin leads to wrinkles, while excessive cell damage promotes an uneven complexion. Therefore, a key step before any prolonged exposure to the sun – whether on the beach, in the mountains or even while walking around the city – is to choose the right protection.
Sunscreen oil: what is it and how does it work?
Sunscreen oil is usually a cosmetic product with a light texture that absorbs quickly and aims to give the skin a “glow” and make it easier to achieve a bronzed complexion. Some oils also contain a certain sun protection factor (SPF), but this is usually low compared to conventional sunscreens. In some cases, sunscreen oil contains natural oils such as coconut, argan, carrot or almond, while some brands also add mineral filters or chemical UV filters to enhance protection.
However, the word “oil” itself often conjures up images of potentially “frying” the skin under intense sunlight, which can lead to uneven protection. While modern sun oils are designed to absorb some of the UV rays, the reality is that they usually can’t match formulas with higher SPFs, especially when it comes to UVA protection. That’s why experts’ advice is always the same: even if you’re using an oil, you should complement it with stronger sunscreens and other precautions.
Benefits of tanning oil
- Nourishing properties: Many formulas are based on vegetable oils that nourish the skin and prevent drying.
- Fast tanning: Oils often help achieve faster “tanning” because they attract the sun’s rays, which is attractive to those who want a bronzed complexion.
- Comfortable application: Most people find the oil easier to spread, and skin often looks silky after application.
Disadvantages and limitations
- Insufficient protection: Most oils do not provide a high SPF, especially in terms of UVA protection, which means that skin can still be exposed to harmful radiation.
- Risk of skin damage: If you rely only on oil and spend too long in the sun, you increase the risk of burns and long-term consequences.
- Possibility of allergies: For sensitive skin, certain ingredients (essential oils, perfumes) may cause irritation.
How to understand SPF and UVA/UVB protection?
Sun Protection Factor, often abbreviated as SPF, indicates how much a product can extend the skin’s natural ability to withstand the sun before it starts to turn red. For example, SPF 30 typically means that skin can be protected 30 times longer than without any protection. However, it’s important to understand that these values are based on laboratory conditions, and real-world factors such as sweating, bathing, and toweling significantly reduce effectiveness.
In addition to SPF, you should also pay attention to the label “broad-spectrum” , which means that the product protects against both UVB and UVA rays. UVB rays (B – burn ) are the main culprits for sunburn, while UVA rays (A – ageing ) are responsible for photoaging and deeper cell damage. A good sunscreen product, whether it is an oil, cream or spray, should have adequate protection against both types of radiation.
Factors influencing the choice of SPF
- Skin phototype: People with lighter skin need a higher SPF, while those with darker skin have slightly higher natural protection, but still need to be careful.
- Sun intensity: The strength of the sun is affected by geographic location, time of day, and season. The midday summer sun can be much more dangerous than the afternoon sun in the spring.
- Length of exposure: If you plan to be outside for more than 15-20 minutes, you need protection even if you are in seemingly “mild” sunlight.
Myths about suntan oil and tanned skin
There are a number of beliefs that for a “good tan” it is necessary to use only oil without any SPF protection. However, it is important to know that even with a high SPF, you can still get a tan, just more slowly and in a healthier way. Sudden darkening and “burning” of the skin usually means that the skin has suffered damage. A tan is, in essence, a defense mechanism of the skin that produces more melanin to protect itself from further damage.
Therefore, if you want a longer-lasting and healthier tan, a better approach is to gradually expose yourself to the sun, using a high sun protection factor. Natural tanning oils can be a supplement, especially if they contain skin-nourishing ingredients, but they should not be your only support. Instead of focusing on getting a quick tan, focus on getting a safe tan , which involves gradually exposing yourself to the sun’s rays and using appropriate protection measures.
The importance of regular application and the correct amount of product
Even if the bottle of oil or cream says SPF 30, it doesn’t mean you’re completely safe all day long. Many people make the mistake of applying it just once, forgetting that the product washes off with sweating, toweling off, or getting into the water. Experts recommend reapplying every 2 hours, especially after swimming. You should also use enough product – the average adult needs about 30 ml of product (about a handful) to cover their entire body.
Natural oils and supplements: what’s safe and what’s not?
Many people like to experiment with natural oils, such as coconut, olive, carrot oil or even cocoa butter, believing that this will protect and nourish the skin. While these can indeed have a nourishing effect and provide minimal protection (usually between SPF 2 and 4), this is by no means enough to prevent skin damage, especially when exposed to the sun’s rays for more than 10-15 minutes.
Also, some oils can cause skin sensitivity when exposed to strong sunlight, especially citrus oils (e.g. lemon oil, bergamot), which can lead to phytophotodermatitis and leave permanent stains on the skin. That’s why it’s always important to check the ingredients of a product that’s advertised as a “natural suntan oil.” The term “natural” alone doesn’t guarantee safety – it’s crucial that the formula has effective filters and provides at least a moderate SPF (e.g. 15 or higher).
Adding aloe vera to your skincare routine
Aloe vera has become synonymous with after-sun skin care, as it has soothing properties, hydrates, and helps repair damaged epidermis. Studies like this one published on PubMed indicate that aloe vera extracts can contribute to skin healing and alleviate inflammatory processes caused by UV radiation.
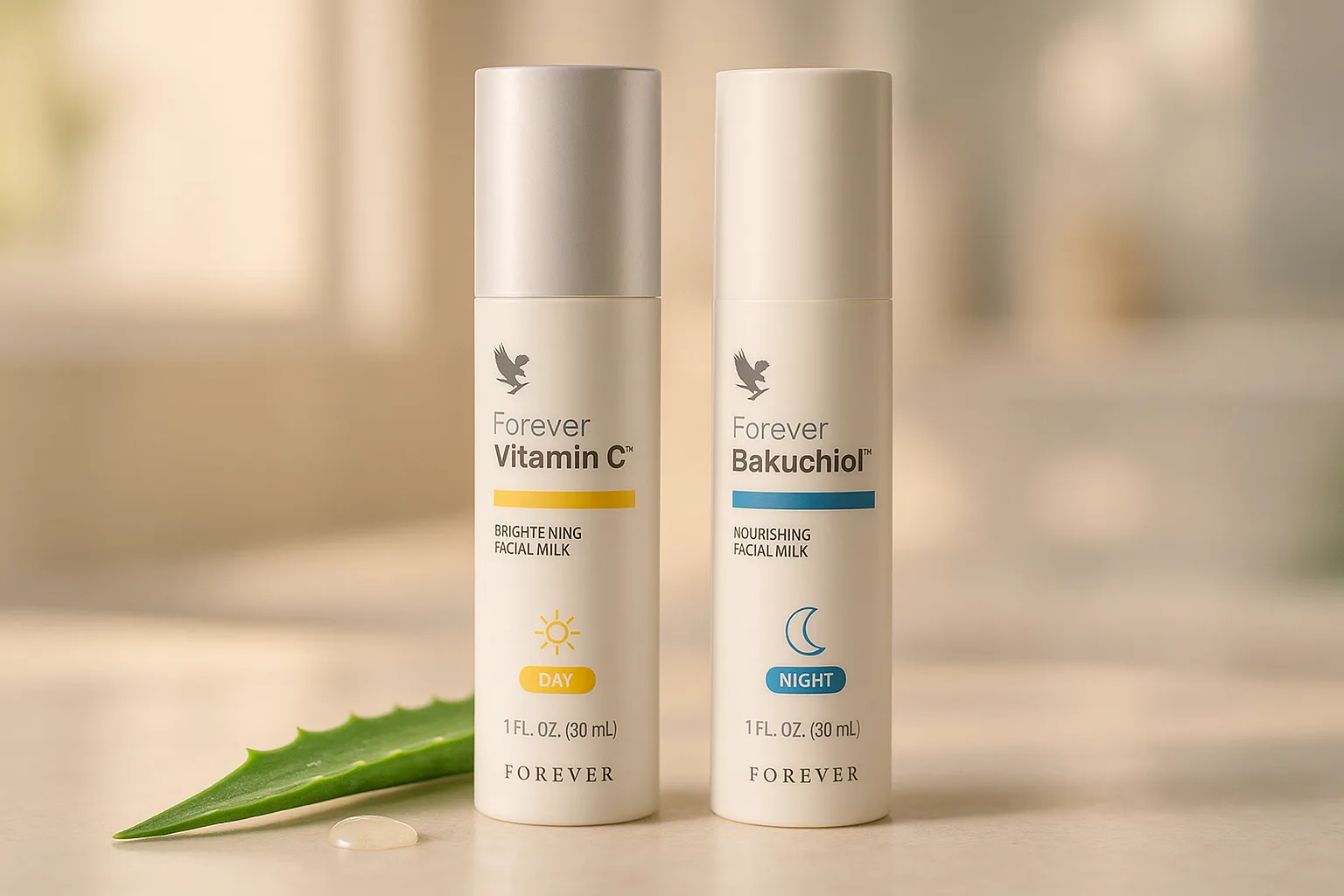
If you enjoy using natural products, you may want to consider a high-quality aloe vera gel. For example, Forever Aloe Vera Gel is one popular product used to moisturize and soothe skin after sun exposure. If you want to learn more about the healing properties and uses of aloe vera, read our article Aloe vera gel – healing properties and uses . However, keep in mind that aloe vera is not a substitute for protection before and during sunbathing, but only a good addition.
Protective measures that go beyond the use of oil
To preserve healthy skin and avoid damage, in addition to choosing the right sunscreen product , pay attention to several other important factors:
1. Limit time spent in the sun
UV radiation is at its peak between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m., depending on your geographic location and time of year. Try to minimize or avoid direct sun exposure during this time. Instead, spend time in the shade and plan your sun exposure early in the morning or late in the afternoon.
2. Clothing and accessories
If you notice that you burn easily, don’t rely solely on cosmetics. Wearing a wide-brimmed hat, sunglasses with UV protection, and long-sleeved, breathable clothing can significantly reduce your exposure. Today, there are also clothing items with UV protection factors, ideal for long periods of time in the sun (for example, UV-protective T-shirts for diving or running).
3. Regular hydration
High temperatures encourage sweating, which increases fluid loss. Dehydration further depletes the skin and makes it more sensitive. Drink plenty of water or natural beverages (watermelon juice, coconut water, herbal teas) to support the skin’s defense mechanisms.
4. Regular application of protective products
We’ve already said it, but it’s worth repeating: even if your product claims to last “8 hours,” it will rub off, melt, and break down under the influence of water, sweat, sea salt, or pool chlorine. Always carry a bottle of oil or cream with you and reapply every two hours (or more often if you’re swimming or sweating a lot).
Routine Supplement: Forever Aloe Sunscreen
If you like to mix and match products, you can try Forever Aloe Sunscreen , which contains aloe vera and SPF 30, providing good protection against both UVB and UVA rays. Many users praise its non-sticky texture and the fact that it also provides hydration to the skin. Compared to typical sun oils, this is a happy medium for some – a moderately lightweight formula, yet a higher level of protection.
You can learn more about the ingredients and benefits of products like Forever Aloe Sunscreen in the article Aloe Sunscreen Cream – Overview and Tips for Use on our website. In any case, whether you choose a product from the Forever Living range or a similar product from another company, make sure that it has a certificate of effective SPF and covers a wide spectrum of UV rays.
Safe sunbathing on different skin types
Every skin is different. People with very fair skin and freckles (phototypes I and II) often react to the sun with redness and can burn very easily. In this case, a suntan oil with a low SPF is not at all advisable. On the other hand, people with darker skin (phototypes IV, V or VI) may not blush as quickly, but this does not mean that they are immune to cumulative damage and an increased risk of skin cancer.
That’s why an individualized approach is key. If you have fair skin or are prone to allergic reactions, experimenting with different oils and minimal SPF can be costly – instead, reach for products that offer high protection (30 or 50+). If you have dark skin, you may be able to use products with a slightly lower SPF (e.g. 15 or 20), but you should still check your skin regularly and avoid overexposure to the strongest sun.
The impact of diet and supplements on skin health
In addition to external protection, diet and nutritional supplements can also help make the skin more resistant to UV radiation. Foods rich in antioxidants , such as berries, green vegetables, nuts and seeds, can help neutralize the free radicals that UV radiation creates in the skin.
Omega-3 fatty acids (e.g. from fish, flaxseed or supplements like Forever Arctic Sea ) may also have an anti-inflammatory effect and contribute to better skin regeneration. Beta-carotene (from carrots, sweet potatoes, apricots) has also been shown to help slightly improve skin’s resistance to UV rays, although it is not a substitute for sunscreen.
If you want a more complex approach, consider including some stress-reducing adaptogenic herbs in your diet (e.g. Forever Multi-Maca ), as chronic stress can also negatively affect your skin. Of course, it’s a good idea to consult a nutritionist or doctor for specific health advice, especially if you have special needs or chronic illnesses.
FAQ – Frequently asked questions about tanning oils
1. Should I apply suntan oil and a high SPF cream at the same time?
It is usually not necessary to apply two products at the same time. If you want to combine, first apply a product with a higher SPF (e.g. a cream), wait for it to absorb, and only then can you apply a light oil. However, it is best practice to choose one quality product that offers protection and care, rather than mixing multiple formulas.
2. Which oil is safest for sunbathing?
There is no universal answer because every skin reacts differently. Oils that contain mineral filters (e.g. titanium dioxide, zinc oxide) and have a confirmed SPF provide better protection. However, always check the label and look for the word “broad-spectrum” and at least SPF 15 or 20. If you have very sensitive skin, you will probably need a higher SPF.
3. Can I use baby oil as sunscreen?
Usually, baby oil or children’s body oils do not have any UV protection, but are intended solely for care. Applying baby oil to the skin before sunbathing is generally not wise, as you can increase the risk of burns. Specialized products with a high protection factor are recommended for children, most often SPF 30 or 50.
4. Why does my skin become dry even after using suntan oil?
Sunscreen may provide a temporary glow, but it may not necessarily deeply moisturize the skin, especially if it contains harsh fragrances or lacks nourishing ingredients. Also, sun exposure dries out the skin, and salt, wind, and chlorine from swimming pools can further aggravate the problem. That’s why it’s always a good idea to apply a moisturizing lotion, cream, or aloe vera gel after sunbathing.
Conclusion: It is crucial to find a balance between beauty and health
Sunscreen and quick tans may be appealing, but we must not forget that maintaining skin health is a long-term priority. Sunburn, premature aging, and an increased risk of melanoma are just some of the problems that can arise if we ignore sun protection advice. The right balance is achieved by using products with sufficient SPF, avoiding the strongest sun during the day, wearing protective clothing, and, of course, taking additional steps like regular moisturizing and aloe vera care.
If you want to explore quality and natural products that can help you care for your skin before and after sunbathing, visit the official Forever store and take advantage of the special offer for a 15% discount . Whether you choose Forever Aloe Sunscreen or another product from the range, the most important thing is to consistently adhere to safe sunbathing habits and avoid extreme conditions without adequate protection.
**This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice. If you have any concerns or health concerns, always consult a doctor or other qualified professional.**