Aloe Vera Barbadensis Miller
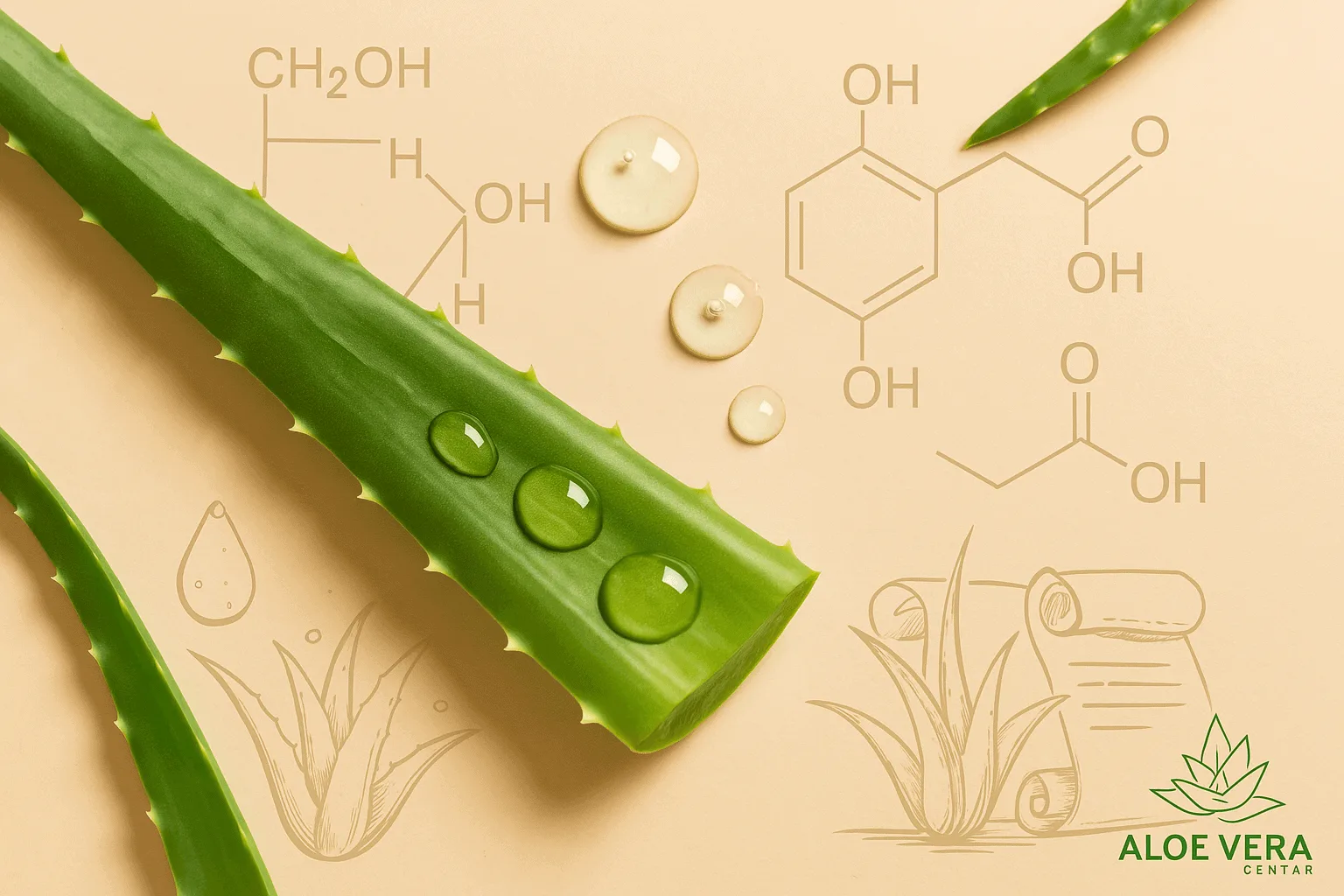
Aloe Vera Composition – Meet the Incredible Natural “Pharmacy”
When we think of a natural plant with incredible medicinal, cosmetic and nutritional properties, few stand out as much as aloe vera . From the cosmetics industry to traditional medicine, this “green elixir” never ceases to fascinate with its effects. However, to fully understand why it is so powerful, it is useful to get to know its chemical structure . It is this structure that introduces us to the world of its active ingredients, which act in synergy as a “natural pharmacy”.
We’ve already talked about the general properties and benefits of aloe vera, but here we’ll focus specifically on the basic ingredients of its gel . Find out how these elements work together in phytotherapy, how they promote regeneration, purification, and immunostimulation, and why aloe vera is the subject of numerous studies in medicine and cosmetics.
Purifying ability – how does aloe vera promote detoxification?
Aloe vera contains potassium and certain sugars specific to this plant, which stands out for its strong laxative and drainage effect. What exactly does that mean?
- Detoxification of the body: Helps to eliminate toxins, excess water and other waste products from the body.
- Supports regular digestion: Thanks to components that stimulate intestinal peristalsis, aloe vera can ease digestive problems and promote regular bowel movements.
- Beneficial for the liver: Some studies mention possible positive effects on the liver, but the exact effects are still being researched.
Of course, for long-term results, regular but moderate intake of aloe vera-based products is recommended, especially fresh, stabilized gel of proven origin.
Aloe vera nutrition – a wide range of active substances
Aloe vera gel is extremely rich in vitamins, minerals, amino acids, and various sugars. Of particular note are:
- Vitamins: Primarily vitamin C, vitamin E and part of the vitamin B complex.
- Minerals: Calcium, magnesium, zinc, manganese, potassium, iron, phosphorus, chromium and others (more about them in a separate chapter below).
- Amino acids: Aloe contains a significant proportion of essential and non-essential amino acids necessary for the construction of proteins and the normal functioning of the organism.
- Sugars (acemannan etc.) – The greatest attention is paid to complex sugars (such as acemannan), which have a number of beneficial effects on immunity and tissue regeneration.
Thanks to such a diverse composition, it is believed that aloe vera can contribute to the overall nutritional status of the body, but care should be taken about the quality of the gel or dietary supplement itself.
The power of wound healing – how aloe vera promotes regeneration
Acemannan , one of the key polysaccharides in aloe, has the ability to stimulate cell renewal and connective tissue production. This practically means:
- Increased collagen production: Collagen is the main building protein of skin and connective tissues, and acemannan encourages cells to create more of it.
- Faster wound healing: The good moisturizing and anti-inflammatory properties of aloe vera can relieve irritation and redness, while also speeding up skin recovery.
- Scar reduction: Regular application of aloe vera gel to minor injuries and scars can help the skin heal faster and maintain elasticity.
This effect is the reason why aloe vera is often found in burn care formulations, as well as in creams and lotions for faster healing of various skin damages.
Antiviral activity and immune system support
Thanks to its complex sugars, primarily acemannan , aloe vera has the ability to support the body’s defense mechanisms. How?
- Purification of blood plasma: Promotes the expulsion of toxins and “waste” from the bloodstream.
- Immunostimulation: Many users of aloe vera notice better resistance and less frequent colds. Research is ongoing in the context of some autoimmune and viral diseases (such as HIV), although they are not yet conclusive.
- Reducing inflammatory processes: The combination of immunomodulatory properties and antioxidants can help balance excessive inflammation in the body.
It is important to note that aloe vera is not a “miracle cure” for all diseases, but rather proves to be a useful addition as part of a holistic approach (healthy diet, appropriate lifestyle, medical treatments when necessary).
Ability to slow down aging – antioxidants in action
Aloe vera naturally contains vitamin C , vitamin E and trace elements such as magnesium and selenium . In combination with amino acids (e.g. proline) and saponins, it helps fight free radicals, which are the main culprits in accelerated cell aging.
Moreover, thanks to this antioxidant effect, aloe vera products are often used in cosmetic lines for mature skin, and regular consumption of aloe gel or juice can also contribute to better hair and nail quality.
Anti-inflammatory effect – mild yet effective
The plant steroids found in aloe vera have the ability to soothe inflammation and redness. In practical terms:
- Topical application: “Cools” areas of damaged or irritated skin (e.g. after an insect bite or minor scratch).
- Reducing swelling: It is sometimes used as a mild “compression” for minor injuries, helping to reduce swelling or itching.
- Dietary supplement: Research is underway to see how regular oral consumption (in gel or juice form) may help control certain inflammatory processes in the digestive system or joints.
Using aloe vera usually does not cause unpleasant side effects, but you need to be careful about the quality of the product and possible allergies.
Antibacterial and antibiotic action
Thanks to cinnamic acid and other phytochemical compounds, aloe vera extract can help cells defend themselves against bacteria.
- Antiseptic properties: Useful for superficial injuries or skin irregularities (acne, minor infections).
- Prevention of bacterial growth: Aloe has been shown in numerous studies to help inhibit the growth of certain pathogenic microorganisms.
In addition, aloamodin , a unique enzyme in aloe, can function as a natural “shield” of the cytoplasm of cells, preventing the penetration of pathogenic germs.
Pain-relieving effect – natural “analgesic” component
Just as aspirin uses salicylic acid to relieve pain and reduce inflammation, aloe vera, thanks to acetylsalicylic acid , has certain antiseptic and analgesic effects.
Of course, the effects are usually mild and depend on the type of discomfort (for example minor surface damage to the skin), but this characteristic makes aloin gel attractive for many “home” preparations and first aid products.
Tumor protection – the role of acemannan and other elements
Particularly interesting are the studies on the combination of potassium, acemannan, vitamin B9 (folic acid), zinc and vitamin B12 in woody aloe, which indicate a potential protective effect against some types of tumors. Although the evidence is still under investigation, the assumption is that:
- Acemanan – Supports the immune system, reducing the risk of uncontrolled cell growth.
- Minerals and vitamins – They help the body’s antioxidant defense and maintain normal cell function.
However, it should be reiterated that aloe vera should not replace classical methods of tumor treatment, but can serve as support within a broader strategy of prevention and healthy eating.
Radiation protection – cell and metabolism renewal
For people undergoing radiotherapy, aloe vera may help with cell regeneration and metabolism. There are reported cases where topical application of aloe gel has reduced skin irritation caused by radiation. This is attributed largely to the “andesthetic” (i.e. soothing and restorative) properties of aloe, although more clinical research is needed to reach a definitive conclusion.
Minerals – a key role in maintaining health
One of the most striking characteristics of aloe vera is the fact that it contains more than twenty essential mineral salts . The most important among them include:
Calcium
The most abundant mineral in the human body; it is essential for bone strength, proper heart function, and muscle contraction. Calcium deficiency can lead to brittle bones (osteoporosis) and heart problems.
Chromium
Critical for controlling blood sugar levels and insulin production. It also affects the metabolism of fatty acids and carbohydrates, helping to maintain a balanced energy system.
Phosphorus
In combination with calcium, it builds and repairs bone tissue. It also participates in energy transfer (ATP) in cells and contributes to normal cell function.
Iron
A key component of hemoglobin, the protein responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to the tissues. Iron deficiency often leads to anemia, weakness, and fatigue.
Manganese
Essential for proper bone development, brain function, and the synthesis of thyroxine (thyroid hormone). It also participates in antioxidant processes that protect cells.
Magnesium
Important for hundreds of biochemical reactions in the body – from protein and nucleic acid metabolism to protecting cells from free radicals. It also helps regulate heart rhythm and muscle function.
Potassium
An essential mineral for maintaining proper blood pH, normal muscle function, and even heart muscle. Potassium works with sodium to remove waste products from cells, and athletes often lose it through increased sweating.
Sodium
It enables the normal functioning of the nervous system and regulates the balance of fluids in the body. Along with potassium, it participates in cellular metabolism.
Zinc
It stimulates tissue regeneration, helps heal wounds and supports over 150 enzyme functions in the body. It is essential for the functioning of cell membranes and the immune system.
Monosaccharides and polysaccharides – “sweet” foundations of energy and immunity
In addition to amino acids and minerals, aloe vera pulp also contains numerous “sugars”:
- Monosaccharides (simple sugars) – For example, mannose and glucose, which serve as a source of energy for our cells.
- Polysaccharides (complex sugars) – The most well-known is acemannan (or carysin). Research suggests that acemannan may play a role in boosting the immune response, killing certain germs and bacteria, and supporting the gastrointestinal tract.
It is no coincidence that many studies consider the potential of acemanan in the fight against diabetes, high cholesterol or even HIV. Although we are still waiting for definitive conclusions, these first results are very promising.
Enzymes – stimulating biochemical reactions
Several important enzymes have been identified in aloe vera that:
- Lipase – Helps break down fats.
- Protease – Breaks proteins into smaller parts (amino acids), facilitating digestion and utilization of nutrients.
- Cellulase – Helps the digestibility of cellulose and utilization of fiber from the diet.
- Catalase – Breaks down toxic hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen, which protects cells from oxidative stress.
- Various phosphates and starch – In smaller amounts, they contribute to metabolism and energy supply.
In this way, aloe vera not only provides valuable nutrients, but also supports their optimal metabolism in the body.
Salicylic acid – a natural ally against inflammation and pain
Salicylic acid (also known as salicylic acid) is one of the main ingredients in aspirin. In aloe vera, it works by:
- Anti-inflammatory and antipyretic – Can help with mild inflammation and fever.
- Anti-acidity of blood platelets – Prevents their aggregation (agglutination), which is beneficial for cardiovascular health.
It is important to note that pharmacological treatments based on pure salicylic acid can sometimes cause irritation of the gastric mucosa or allergic reactions. Using aloe, which also contains other soothing components, may be a milder alternative, but it is still advisable to pay attention to possible individual reactions.
Lignin and saponin – the hidden power of plant tissue
The chemical composition of aloe vera gel also includes:
- Lignin (C 10 H 13 O 13 ) – Responsible for the yellowish tones and hardening of plant tissue. The highest concentrations are found in the outer parts of the leaf, and it helps in the structural strength of the plant.
- Saponin – A biological compound with pronounced cleaning and antiseptic properties. It forms foam when in contact with water, indicating its ability to break down fats (saponification). It also contributes to digestive processes and “softens” tissue.
Many plants, such as horsetail, licorice, and ginseng, also contain saponins, but in aloe vera, this component is often highlighted for its contribution to “detox” and protective properties.
Where can I find more information about aloe?
There are many aloe vera lovers, and there are detailed instructions and articles that talk about 100% natural Aloe Vera Barbadensis Miller. If you decide to grow the plant yourself at home, pay attention to the conditions of heat, light and moderate watering. You can find tips here .
Aloe Vera and a business opportunity – discover the partnership with Forever Living
In the modern world, aloe vera is not only a symbol of health, but also an opportunity to develop an online business . Brands like Forever Living Products offer the possibility of cooperation and distribution of proven aloe-based products, and thus the opportunity for financial independence.
If you want to learn more, get to know the work of our team and see how aloe vera fits into a unique business model, just click
here and watch a short video. It could be your first step towards a new chapter in life – one where your passion for natural products merges with business success.
FAQ – most frequently asked questions about the composition and use of aloe vera
1. Can aloe vera “cure” me of certain diseases?
Aloe vera offers support and assistance in regeneration and boosting immunity, but it is not a miracle cure for serious or chronic illnesses. It is always advisable to consult a doctor, especially for serious health conditions.
2. Are all parts of aloe the same quality?
No. The gel from the inner part of the leaf is the most valuable ingredient for most uses, while the latex (sap) just below the bark contains anthraquinones that can cause a strong laxative effect. Quality manufacturers often remove the latex to reduce the risk of adverse reactions.
3. What are the possible side effects of long-term use of aloe?
If the products are misused or if uncontrolled amounts of latex are taken, digestive problems such as diarrhea may occur. Also, allergic reactions, although rare, can occur in sensitive people. Always choose proven products and follow the recommended doses.
4. Can consuming aloe help with weight loss?
Aloe vera can contribute to better digestion and increased detoxification of the body, which sometimes helps with body weight regulation. However, a healthy diet and regular activity are still key, and aloe serves as an additional support, not as a “main” factor.
Conclusion
The composition of aloe vera is extremely complex. From vitamins , minerals and amino acids , to enzymes and complex polysaccharides (such as acemannan), to plant steroids and anti-inflammatory substances – the entire “palette” of compounds makes this plant an indispensable ally in cosmetic and health routines around the world. However, it is always worth remembering that product quality and rational dosage play a key role.
Precisely because of its unique chemical structure, aloe vera is the subject of continuous research, both in terms of health care and disease prevention, and as an ingredient in premium cosmetic formulas. If you want to take advantage of its benefits in a business sense, there is a way to join a team that combines a passion for natural solutions and building a stable online business.
Aloe Vera Barbadensis Miller, with its rich history and supported by modern knowledge, remains a plant that delights again and again. Whether you grow it at home or rely on proven products, you will enjoy its powerful potential for body care, skin care, immune support and much more.
This content is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. For specific health conditions, side effects, or combination with therapies, please consult a qualified professional.